Features of Android - 13
Themed app icons :
Android 13 extends Material You dynamic color to all app icons, letting users opt-in to icons that inherit the tint of their wallpaper and other theme preferences. All your app needs to supply is a monochromatic app icon and a tweak to the adaptive icon XML.
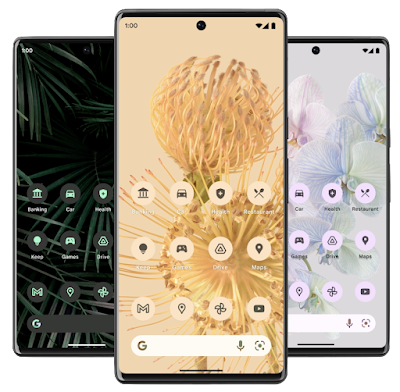 |
| Themed app icons adapting to wallpapers colors and dark theme (left). |
 |
| Per-app languages in Settings |
 |
| Improved line height for non-Latin scripts in apps targeting Android 13 (bottom). |
 |
COLRv1 vector emoji (left) and bitmap emoji. |
Programmable shaders :
Media controls derived from PlaybackState:
 |
Android 13 media controls are consistent on phones and tablets. |
Bluetooth LE Audio:
Low Energy (LE) Audio is the next-generation wireless audio built to enable new use cases like sharing and broadcasting audio to friends and family, or subscribing to public broadcasts for information, entertainment, or accessibility. It’s designed to ensure that users can receive high fidelity audio without sacrificing battery life, and lets them seamlessly switch between different use cases. Android 13 adds built-in support for LE Audio, so developers can use the new capabilities on compatible devices.
MIDI 2.0 - Android 13 adds support for the new MIDI 2.0 standard, including the ability to connect MIDI 2.0 hardware through USB. This updated standard offers features such as increased resolution for controllers, better support for non-Western intonation, and more expressive performance using per-note controllers.
OpenJDK 11 updates :
Android 13 Core Libraries now align with the OpenJDK 11 LTS release, with both library updates and Java 11 programming language support for app and platform developers. We plan to bring these Core Library changes to more devices through Google Play system updates, as part of an ART module update for devices running Android 12 and higher.
Predictive back gesture - Android 13 introduces new APIs that let your app tell the system that it will handle back events in advance, a practice we call the "ahead-of-time" model. This new approach is part of a multi-year effort to help you prepare your app to support the predictive back gesture, which is available for testing in this release through a developer option.
Built for tablets
Android 13 extends the 12L update that we released earlier this year, and it delivers an even better experience on tablets. You’ll find features like an enhanced multitasking taskbar, more large-screen layouts and optimizations in system UI and apps, improved compatibility modes for apps, and more. We’re continuing to invest to give you the tools you need to build great experiences for tablets as well as Chromebooks and foldables. You can learn more about how to get started optimizing for large screens, and be sure to check out our large screens developer resources.
 |
| Multitasking on tablets with Android 13. |
Privacy and security
Photo picker and APIs - A new system photo picker now gives users a standard, privacy-protecting way to share local and cloud-based photos. Photo picker extends Android’s long-standing document picker and makes it easy for users to share specific photos and videos with an app, without giving the app permission to view all media files on the device. Photo picker provides a dedicated experience for photos and videos and includes APIs for apps to access the shared media files. The photo picker experience is now available to users who receive Google Play system updates, on devices (excepting Go devices) running Android 11 and higher. |
Photo picker lets users share specific photos and videos with an app. |
 |
| Notification permission dialog in Android 13. |
Nearby device permission for Wi-Fi - Android 13 introduces the NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES runtime permission for apps that manage a device's connections to nearby access points over Wi-Fi. The new permission is required for many commonly-used Wi-Fi APIs and enables apps to discover and connect to nearby devices over Wi-Fi without also needing to acquire the location permission.
Granular permissions for media file access :
Safer exported Intent filters - Android 13 applies stricter rules when delivering explicit intents to exported intent filters in another app that’s targeting Android 13. For intents that specify actions, the system now delivers the intents to the exported component only if the intent matches the receiver’s declared <intent-filter> elements.
Performance for apps:
Android 13 improves performance and efficiency for all apps through updates to the ART runtime. We plan to bring these improvements to more Android users through Google Play system updates, as part of our ongoing ART module updates for devices running Android 12 and higher.Improved garbage collection - A new garbage collector based on the Linux kernel feature userfaultfd is coming to ART on Android 13 devices in an upcoming Google Play system update. The new garbage collector eliminates the read barrier and its fixed overhead per object loaded, reducing memory pressure and leading to as much as ~10% reduction in compiled code size. It’s more efficient at GC-time as well, since pages are freed as compaction progresses. Overall, the new garbage collector helps to save battery, avoid jank during GC operations, and protect apps from low-memory kills.
Optimizations throughout ART - In Android 13, ART makes switching to and from native code much faster, with JNI calls now up to 2.5x faster. We’ve also reworked the runtime’s reference processing to make it mostly non-blocking, which further reduces jank. We’ve exposed a new public API, Reference.refersTo(), which is useful in reclaiming unreachable objects sooner, and we’ve made the interpreter faster by optimizing class/method lookups. Lastly, ART now performs more byte-code verification at install time, avoiding the expense of verification at runtime and keeping app startup times fast.




Comments
Post a Comment